Large Language Models (LLMs) are remarkable tools with impressive capabilities. Since ChatGPT's launch in 2022, the AI landscape has exploded with powerful models like Claude Sonnet, GPT-4, Gemini, and many others, each attracting millions of users. The key to their remarkable performance lies in a crucial element: prompt engineering.
Why Prompts Matter
Modern LLMs like ChatGPT, Claude Sonnet, and GPT-4 excel at understanding and mimicking human conversation nuances. They're trained on diverse internet text, enabling them to generate creative responses, navigate complex dialogues, and even exhibit humor. However, it's important to note that these models don't truly understand or have beliefs; they generate responses based on patterns learned during training.
LLMs generate output based on statistical patterns learned from vast amounts of data, without having an inherent understanding of what is true or false. They operate by analyzing prompts as sequences of tokens representing the input text. You can see this tokenization process in action using tools like OpenAI's Tokenizer or Anthropic's Claude interface.
Understanding Tokenization
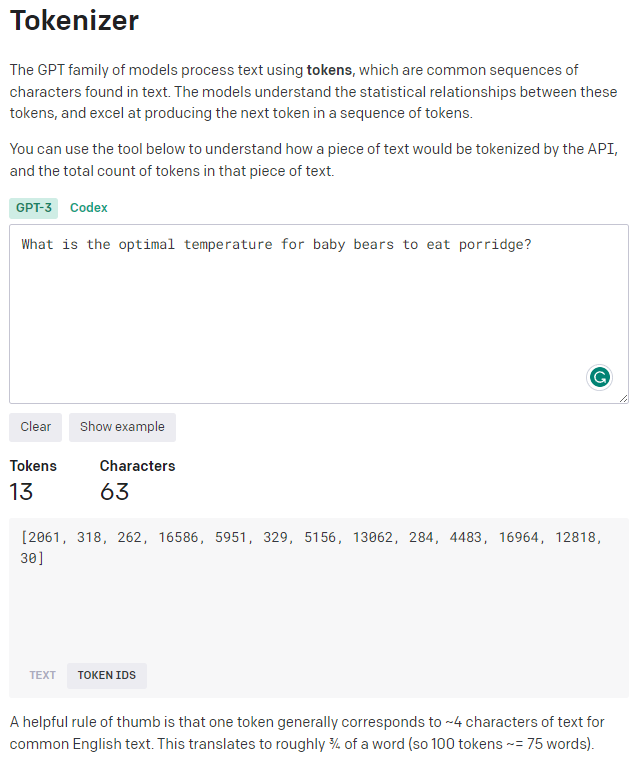
These models use token sequences to predict the most likely continuation, drawing upon patterns learned during training. They cannot reason or comprehend the deeper meaning behind the information they generate.
Understanding how LLMs work is crucial to using them effectively. Whether you're working with ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, or other models, they can be valuable tools for generating code, unit tests, boilerplate methods, and various language-related tasks. As with any tool, it's up to the user to cross-check outputs for accuracy and validity, particularly for critical or factual information.
The Three Bears of Prompt Engineering

Remember Goldilocks and the three bears? Just like she discovered with the porridge, prompt engineering follows the same principle: too little context leaves LLMs confused, too much context overwhelms them, but just the right amount creates perfect results.
Let's explore how Papa Bear, Mama Bear, and Baby Bear teach us the art of balanced prompt crafting across different LLM platforms.
Papa Bear: Too Little Context
Papa Bear's approach is too sparse—brief, vague prompts that leave LLMs guessing about your intent. Without sufficient context, AI models like ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini struggle to understand what you actually want, often producing irrelevant or generic responses.
"Temperature?"
This prompt is too vague—temperature of what? For what purpose? Any LLM has no context to work with.
Mama Bear: Too Much Context
Mama Bear overwhelms LLMs with excessive detail and unnecessary backstory. While context is important, too much information can bury your actual request, leading to verbose, unfocused responses that miss the mark—regardless of whether you're using ChatGPT, Claude, or another model.
"In the cozy little cottage on the hill, where the fireplace crackles and the night is chilly, surrounded by memories of childhood and the warmth of family gatherings, what is the optimal temperature for the porridge to warm our souls and tummies while we sit around the wooden table that's been in the family for generations?"
This prompt is buried in unnecessary details that distract from the core question.
Baby Bear: Just the Right Context
Baby Bear strikes the perfect balance—providing clear, concise context that gives any LLM exactly what it needs to understand your intent without overwhelming it with unnecessary details. This is the sweet spot of prompt engineering across all platforms.
"What is the optimal serving temperature for porridge to ensure it's safe to eat but not too hot for a child?"
This prompt is specific, clear, and provides just enough context for a focused, useful response.
Goldilocks Principle
Avoid being too vague or overwhelming with your prompts. Strike the Goldilocks balance: not too little, not too much, but just the right amount of context to get the point across and achieve the best results.
Improving LLM Prompt Crafting
Universal Prompt Engineering Tips
- Use clear language—be explicit about your requirements and expectations across all LLM platforms
- Be concise—avoid overly complex or lengthy prompts that work poorly on any model
- Iterate and experiment—refine prompts to fine-tune outputs for your specific LLM
- Be specific to your domain (e.g., Python, JavaScript) when needed
- Include code samples for programming-related queries
- Clarify the objective and desired output format
- Ask for best practices or step-by-step guidance
- Pose real-world problem-solving scenarios with context
- Request comparisons between different approaches or technologies
- Ask for debugging help with specific error messages
- Explore advanced features and design patterns in your field
- Consider the strengths of different models (e.g., Claude for reasoning, GPT for creativity)
Mastering prompt engineering is pivotal in harnessing the true potential of any Large Language Model. By providing clear instructions and relevant context, we can leverage these tools—whether ChatGPT, Claude Sonnet, Gemini, or others—to make us better developers, writers, and problem-solvers.
Prompt Engineering
Prompt Engineering is the art of crafting precise, effective prompts to guide AI models like ChatGPT, Claude Sonnet, Gemini, and other LLMs toward generating cost-effective, accurate, useful, and safe outputs. It's not confined to text generation but has wide-ranging applications across the AI domain. Prompt engineering is essential for creating better AI-powered services and obtaining superior results from existing generative AI tools.
Prompt engineers play a vital role in optimizing AI models' efficiency and cost-effectiveness. They can access various models through different APIs—OpenAI's GPT models, Anthropic's Claude, Google's Gemini, and others—each with unique cost structures and capabilities. Parameter tuning and prompt optimization are essential for improving response quality and accuracy across different platforms.
Prompt design involves creating the perfect prompt for a language model to achieve a stated goal. It considers each model's unique nuances, domain knowledge, and quality measurement criteria. Modern prompt engineering extends this to include designing prompts at scale, tool integration, workflow planning, prompt management, evaluation, and optimization across multiple LLM platforms.
Key Takeaway
Prompt engineering is the key to unlocking the full potential of AI models like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and others, with applications ranging from customer support to content creation, coding, education, and beyond.
LLM-Specific Considerations
ChatGPT & GPT Models
- Excellent for creative writing and brainstorming
- Strong code generation capabilities
- Responds well to conversational prompts
- Custom instructions for personalization
Claude Sonnet & Opus
- Superior reasoning and analysis
- Excellent for complex problem-solving
- Great at following detailed instructions
- Handles long-form content exceptionally well
Google Gemini
- Strong multimodal capabilities
- Excellent for factual information
- Good at structured data tasks
- Integrates well with Google services
Open Source Models
- Llama, Mistral, and others
- Customizable for specific domains
- Cost-effective for high-volume use
- Full control over deployment and data
Custom Instructions and System Prompts
Most modern LLMs support some form of custom instructions or system prompts that allow you to set persistent guidelines for your interactions. These personalized directives help the AI understand your preferences and provide responses that align with your specific requirements.
Custom instructions are personalized guidelines you can set to influence AI responses across different platforms. They serve as directives to help models understand your preferences and provide responses that align with your requirements—whether you're using ChatGPT's Custom Instructions, Claude's system prompts, or similar features in other models.
These instructions can be especially useful when you have specific expectations for the content, style, or format of responses. By utilizing custom instructions, you can ensure that AI models generate responses that are more in line with your desired outcomes across different platforms.
Setting Up Custom Instructions
- ChatGPT: Use Custom Instructions in settings to set persistent preferences
- Claude: Begin conversations with system prompts or use project-specific instructions
- API Usage: Include system messages in your API calls for consistent behavior
- Open Source: Configure system prompts during model initialization
Whether you're looking for code solutions, explanations, or engaging conversations, custom instructions can be your key to a more personalized and productive experience across different LLM platforms.
Custom instructions are a powerful feature that can significantly improve your interactions with any LLM. The suggestions provided in this article are universal principles that you can adapt to your specific requirements and preferred AI platform.